

The beekeeping industry is constantly changing as the demands for bees, and their beekeepers also change. Innovation in beekeeping is welcome as this seemingly ancient industry evolves to deal with the threats our bees face.
It seems like varroa mites have been around forever, but they are a fairly young threat to bees that started in the late 1980s. Fortunately, beekeepers have help from an industry that wants to partner with them to help deal with this threat.
There have been a variety of varroa mite treatments available, and we have better options than beekeepers in the 80s or 90s do.
The beekeeping industry is constantly changing as the demands for bees, and their beekeepers also change. Innovation in beekeeping is welcome as this seemingly ancient industry evolves to deal with the threats our bees face.
It seems like varroa mites have been around forever, but they are a fairly young threat to bees that started in the late 1980s. Fortunately, beekeepers have help from an industry that wants to partner with them to help deal with this threat.
There have been a variety of varroa mite treatments available, and we have better options than beekeepers in the 80s or 90s do.

In 2023, Veto-Pharma, the maker of the popular varroa mite treatment Apivar, came out with a new formula. Apivar has been available in the US since 2013 and has worked well for beekeepers as a part of the normal varroa treatment rotation.
Apivar uses the active ingredient Amitraz which is approved by the EPA to be used to control varroa mites in honey bee colonies. This formula requires a 2-month treatment period because of its slow-release formula using plastic strips.
This has worked well and continues to work well, but the beekeeping industry requires a new formula to meet the needs of commercial beekeepers. There are other options besides Amitraz like Hopguard, Formic Pro and Apiguard. They all work differently, and it’s wise to use these chemicals on rotation.

In 2023, Veto-Pharma, the maker of the popular varroa mite treatment Apivar, came out with a new formula. Apivar has been available in the US since 2013 and has worked well for beekeepers as a part of the normal varroa treatment rotation.
Apivar uses the active ingredient Amitraz which is approved by the EPA to be used to control varroa mites in honey bee colonies. This formula requires a 2-month treatment period because of its slow-release formula using plastic strips.
This has worked well and continues to work well, but the beekeeping industry requires a new formula to meet the needs of commercial beekeepers. There are other options besides Amitraz like Hopguard, Formic Pro and Apiguard. They all work differently, and it’s wise to use these chemicals on rotation.
Amiflex: A New Formula For Treating Varroa Mites
Amiflex: A New Formula For Treating Varroa Mites
Veto-Pharma announced in April 2023 a new formula of their already successful Amitraz formula, which is available from Foxhound Bee Company. The new formula uses the EPA-approved Amitraz in an innovative mode that is easy and quick to apply.
Amiflex is for sale directly from us but requires a Pesticide Applicator License, which can be purchased from your state. More on that below. Amiflex is considered a Restricted Use Pesticide (RUP), so it can only be handled by certified applicators.
Veto-Pharma announced in April 2023 a new formula of their already successful Amitraz formula, which is available from Foxhound Bee Company. The new formula uses the EPA-approved Amitraz in an innovative mode that is easy and quick to apply.
Amiflex is for sale directly from us but requires a Pesticide Applicator License, which can be purchased from your state. More on that below. Amiflex is considered a Restricted Use Pesticide (RUP), so it can only be handled by certified applicators.
Easy To Apply
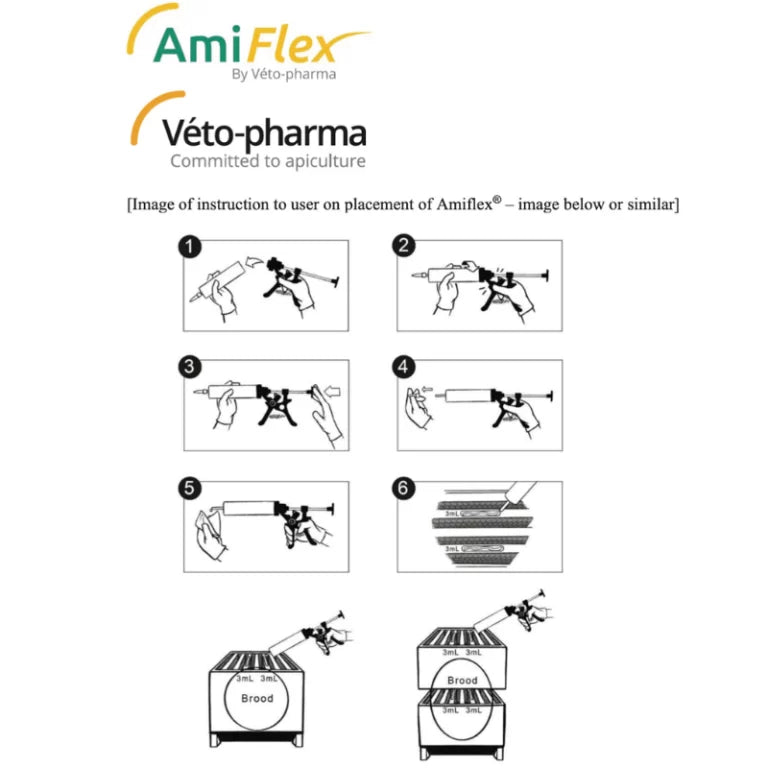
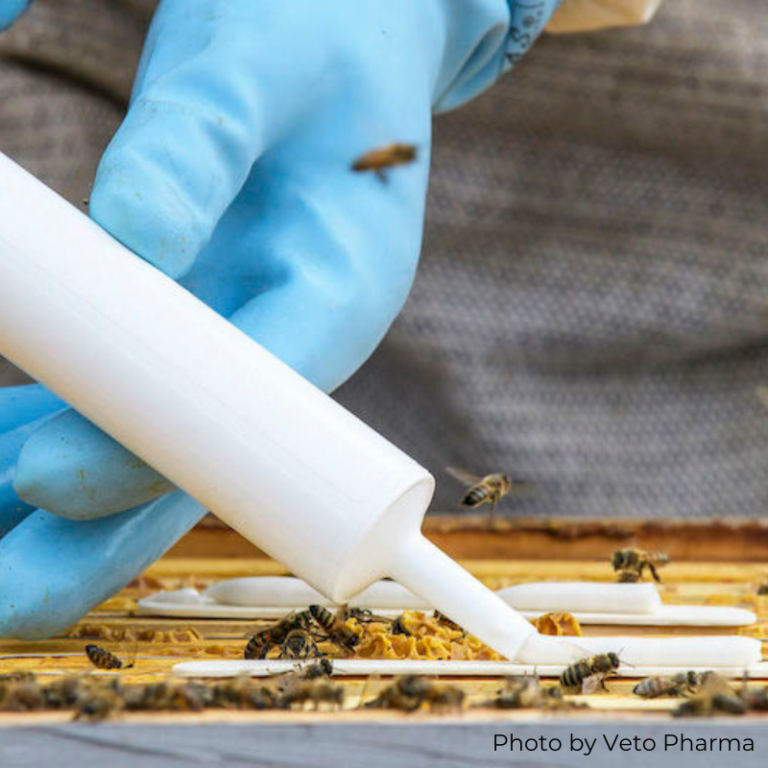
Amiflex is a gel that is applied using a device similar to a caulk gun, providing the proper does with each application.
This dosing strategy is ideal for commercial and sideliner beekeepers as the treatment can be added quickly at an affordable price with low labor.
The 120ml cartridge applies an accurate 3 ml dose of Amiflex gel each time it is applied to the top bars on the included wooden sticks. For a single brood box, 6 ml is the dose.
For a double brood box, 12ml is the dose. When treating with a double brood box, the 12ml dose is applied with 2, 3ml lines in the bottom box and 2, 3ml lines in the top box.
This formula of Amitraz is not temperature sensitive and can be used any time of the year the honey bees are active.
Easy To Apply

Amiflex is a gel that is applied using a device similar to a caulk gun, providing the proper does with each application.
This dosing strategy is ideal for commercial and sideliner beekeepers as the treatment can be added quickly at an affordable price with low labor.
The 120ml cartridge applies an accurate 3 ml dose of Amiflex gel each time it is applied to the top bars on the included wooden sticks. For a single brood box, 6 ml is the dose.
For a double brood box, 12ml is the dose. When treating with a double brood box, the 12ml dose is applied with 2, 3ml lines in the bottom box and 2, 3ml lines in the top box.
This formula of Amitraz is not temperature sensitive and can be used any time of the year the honey bees are active.
Websites For Pesticide Applicator License Information
Websites For Pesticide Applicator License Information
- Federal EPA: Pesticide Applicator Certification
- Alabama: Alabama Agriculture & Industries – Pesticide Management
- Alaska: Alaska Department of Environmental Conservation
- Arizona: University of Arizona – Agricultural Pesticide Certification Training
- Arkansas: University of Arkansas – Pesticide Application Training
- California: California Department of Pesticide Regulation
- Colorado: Colorado Department of Agriculture
- Connecticut: Connecticut Department of Energy & Environmental Protection
- Delaware: Delaware Department of Agriculture
- District of Columbia: DC Department of Energy & Environment
- Florida: Florida Department of Agriculture
- Georgia: Georgia Professional Certifications
- Hawaii: Hawaii Department of Agriculture
- Idaho: Idaho Division of Agricultural Resources
- Illinois: Illinois Pesticide Certification and Licensing
- Indiana: Office of Indiana State Chemist – Pesticide Section
- Iowa: Iowa State University Extension
- Kansas: Kansas Department of Agriculture
- Kentucky: University of Kentucky – Entomology
- Louisiana: Louisiana Department of Agriculture and Forestry
- Maine: Maine Department of Agriculture, Conservation and Forestry
- Maryland: Maryland OneStop
- Massachusetts: Massachusetts Government
- Michigan: Michigan State University Extension
- Minnesota: University of Minnesota Extension
- Mississippi: Mississippi State University Extension Service
- Missouri: University of Missouri Extension
- Montana: Montana State University – Pesticide Education Program
- Nebraska: University of Nebraska – Pesticide Safety Education Program
- Nevada: Nevada Department of Agriculture
- New Hampshire: New Hampshire Department of Agriculture, Markets & Food
- New Jersey: New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection
- New Mexico: New Mexico Department of Agriculture
- New York: USDA ARS
- North Carolina: North Carolina Department of Agriculture
- North Dakota: North Dakota Department of Agriculture
- Ohio: Ohio Department of Agriculture
- Oklahoma: Oklahoma Department of Agriculture
- Oregon: Oregon Department of Agriculture
- Pennsylvania: Penn State Extension
- Rhode Island: Rhode Island Department of Environmental Management
- South Carolina: Clemson University – Pesticide Regulation
- South Dakota: South Dakota Department of Agriculture and Natural Resources
- Tennessee: Tennessee Department of Agriculture
- Texas: Texas A&M University – School Integrated Pest Management
- Utah: Utah Department of Agriculture and Food
- Vermont: Vermont Agency of Agriculture, Food & Markets
- Virginia: Virginia Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services
- Washington: Washington State Department of Agriculture
- West Virginia: West Virginia Department of Agriculture
- Wisconsin: University of Wisconsin – Pesticide Applicator Training Program
- Wyoming: Wyoming Department of Agriculture Pesticide Program
- Federal EPA: Pesticide Applicator Certification
- Alabama: Alabama Agriculture & Industries – Pesticide Management
- Alaska: Alaska Department of Environmental Conservation
- Arizona: University of Arizona – Agricultural Pesticide Certification Training
- Arkansas: University of Arkansas – Pesticide Application Training
- California: California Department of Pesticide Regulation
- Colorado: Colorado Department of Agriculture
- Connecticut: Connecticut Department of Energy & Environmental Protection
- Delaware: Delaware Department of Agriculture
- District of Columbia: DC Department of Energy & Environment
- Florida: Florida Department of Agriculture
- Georgia: Georgia Professional Certifications
- Hawaii: Hawaii Department of Agriculture
- Idaho: Idaho Division of Agricultural Resources
- Illinois: Illinois Pesticide Certification and Licensing
- Indiana: Office of Indiana State Chemist – Pesticide Section
- Iowa: Iowa State University Extension
- Kansas: Kansas Department of Agriculture
- Kentucky: University of Kentucky – Entomology
- Louisiana: Louisiana Department of Agriculture and Forestry
- Maine: Maine Department of Agriculture, Conservation and Forestry
- Maryland: Maryland OneStop
- Massachusetts: Massachusetts Government
- Michigan: Michigan State University Extension
- Minnesota: University of Minnesota Extension
- Mississippi: Mississippi State University Extension Service
- Missouri: University of Missouri Extension
- Montana: Montana State University – Pesticide Education Program
- Nebraska: University of Nebraska – Pesticide Safety Education Program
- Nevada: Nevada Department of Agriculture
- New Hampshire: New Hampshire Department of Agriculture, Markets & Food
- New Jersey: New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection
- New Mexico: New Mexico Department of Agriculture
- New York: USDA ARS
- North Carolina: North Carolina Department of Agriculture
- North Dakota: North Dakota Department of Agriculture
- Ohio: Ohio Department of Agriculture
- Oklahoma: Oklahoma Department of Agriculture
- Oregon: Oregon Department of Agriculture
- Pennsylvania: Penn State Extension
- Rhode Island: Rhode Island Department of Environmental Management
- South Carolina: Clemson University – Pesticide Regulation
- South Dakota: South Dakota Department of Agriculture and Natural Resources
- Tennessee: Tennessee Department of Agriculture
- Texas: Texas A&M University – School Integrated Pest Management
- Utah: Utah Department of Agriculture and Food
- Vermont: Vermont Agency of Agriculture, Food & Markets
- Virginia: Virginia Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services
- Washington: Washington State Department of Agriculture
- West Virginia: West Virginia Department of Agriculture
- Wisconsin: University of Wisconsin – Pesticide Applicator Training Program
- Wyoming: Wyoming Department of Agriculture Pesticide Program
7-Day Flash Treatment
7-Day Flash Treatment
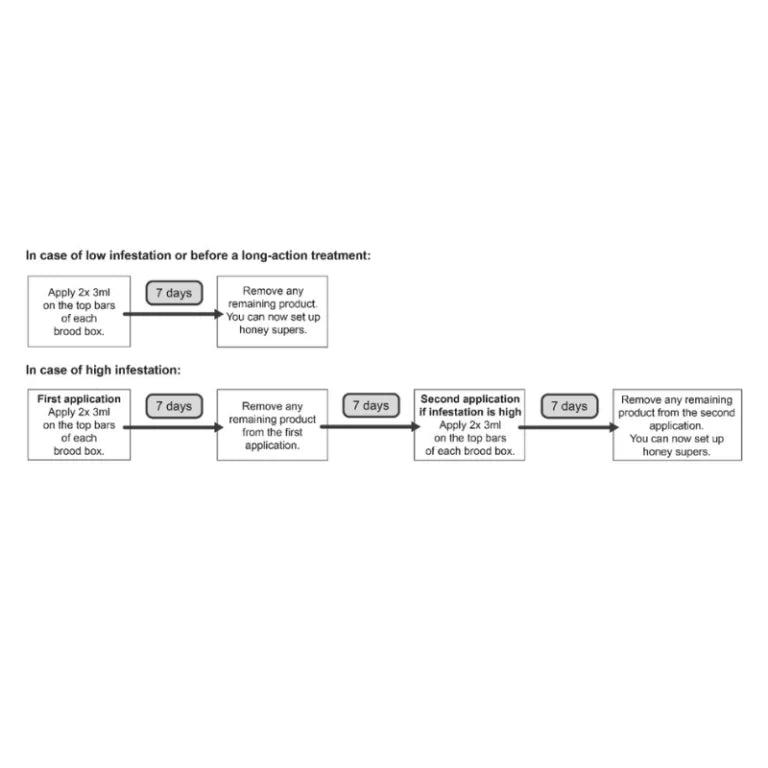
Designed to meet the needs of commercial beekeepers, Amiflex can be used before, after or in-between honey flows. This timing would work great after pollination while in transport from the next location.
Because the active ingredient is Amitraz, Amiflex should only be used when honey supers are not present. A second treatment can be applied with a 7-day break between treatments.
A single hive can be treated 4 times a year. It is recommended to combine a flash treatment of Amiflex with a follow up treatment of the slow-release Apivar for a long-lasting varroa treatment.
Designed to meet the needs of commercial beekeepers, Amiflex can be used before, after or in-between honey flows. This timing would work great after pollination while in transport from the next location.
Because the active ingredient is Amitraz, Amiflex should only be used when honey supers are not present. A second treatment can be applied with a 7-day break between treatments.
A single hive can be treated 4 times a year. It is recommended to combine a flash treatment of Amiflex with a follow up treatment of the slow-release Apivar for a long-lasting varroa treatment.
Stumble
UponReddit
Stumble
UponReddit
Alternative To Illegal Varroa Treatments
Alternative To Illegal Varroa Treatments
It has become common for commercial beekeepers to buy unregulated versions of Amitraz to create their varroa treatments. The efficacy of the treatments varies by the source of amitraz, how it is mixed, how it is stored, and how it is applied.
The inconsistencies lead to misuse of the amitraz and possible resistance to bees. The EPA has enforced the laws against the misuse of amitraz, and Amiflex is a legal and alternative solution to illegal amitraz.
Other mite treatments like Apistan and Checkmite+ have lost their efficacy from misuse by beekeepers, so having a controlled, consistent treatment is important to the future of beekeeping.
It has become common for commercial beekeepers to buy unregulated versions of Amitraz to create their varroa treatments. The efficacy of the treatments varies by the source of amitraz, how it is mixed, how it is stored, and how it is applied.
The inconsistencies lead to misuse of the amitraz and possible resistance to bees. The EPA has enforced the laws against the misuse of amitraz, and Amiflex is a legal and alternative solution to illegal amitraz.
Other mite treatments like Apistan and Checkmite+ have lost their efficacy from misuse by beekeepers, so having a controlled, consistent treatment is important to the future of beekeeping.
Safe For Bees And Beekeepers
Historically, the only option beekeepers had for a flash treatment for varroa mite control has been oxalic acid vaporization or Formic Pro. Oxalic acid works great to kill varroa mites on adult bees but does not work on mites in the cells. Formic Pro works quickly but is temperature sensitive and is a 14-day treatment.
Amiflex has been approved for use in a honey bee colony because it is not harmful to the beekeeper or applicator and does not leave residues in honey above the EPA thresholds.
The 6 years of research by Veto Pharma to develop Amiflex have proven it has no impact on the bee population, queen, or brood development.

Safe For Bees And Beekeepers
Historically, the only option beekeepers had for a flash treatment for varroa mite control has been oxalic acid vaporization or Formic Pro. Oxalic acid works great to kill varroa mites on adult bees but does not work on mites in the cells. Formic Pro works quickly but is temperature sensitive and is a 14-day treatment.
Amiflex has been approved for use in a honey bee colony because it is not harmful to the beekeeper or applicator and does not leave residues in honey above the EPA thresholds.
The 6 years of research by Veto Pharma to develop Amiflex have proven it has no impact on the bee population, queen, or brood development.
Amiflex Packaging
Amiflex Packaging
Amiflex is due to be available in the US in the summer of 2023 and will be available in multiple sizes. The packaging is designed for commercial beekeepers.
- Starter Pack – Treats 100 double deeps or 200 single deeps
- Includes 1 dosing gun, 10 (120ml) cartridges, and 400 wooden sticks
- Refill Pack – Treats 100 double deeps or 200 single deeps
- 10 (120 ml) cartridges and 400 wooden sticks
For more details on Amiflex, see the Amiflex Veto Pharma page.
Check out our Vlog: Comparing The Best Oxalic Acid Vaporizer: Corded vs Battery For Varroa Mite Vaporization.
Amiflex is due to be available in the US in the summer of 2023 and will be available in multiple sizes. The packaging is designed for commercial beekeepers.
- Starter Pack – Treats 100 double deeps or 200 single deeps
- Includes 1 dosing gun, 10 (120ml) cartridges, and 400 wooden sticks
- Refill Pack – Treats 100 double deeps or 200 single deeps
- 10 (120 ml) cartridges and 400 wooden sticks
For more details on Amiflex, see the Amiflex Veto Pharma page.
Check out our Vlog: Comparing The Best Oxalic Acid Vaporizer: Corded vs Battery For Varroa Mite Vaporization.